Ever questioned how your system of air conditioning manages to keep your home or place of work cool during the blazing summers? Want to know How AC works? You might be surprised to learn that your refrigerator and air conditioner function mainly in the same way. The main distinction is that while an air conditioner maintains a suitable temperature in your house, workplace, or business space, a refrigerator only cools a small, insulated room.
For more services visit: AC maintenance Dubai
An air conditioner is one component of a central heating and cooling system that transfers heat energy from the exterior of the house. An air conditioner is a central heating and cooling system that distributes cool air through sheet metal ductwork by drawing warm air from within, eliminating its heat, and replacing it with cooler air.
An Air Conditioner’s Components
The first step in understanding How AC works is becoming familiar with its many components. Here are the four essential parts of excellent and sufficient cooling around your home. Listed simply for your convenience:
1- Refrigerant:
This chemical, sometimes known as coolant, is vital to the air conditioner’s operation. It must transport the heat outdoors and discharge it into the environment. The refrigerant moves through the different parts of the unit and undergoes modifications as it does so during the cooling cycle.
More service: AC installation in Dubai
2- Evaporator Coils:
The primary function of the indoor unit is to absorb the heat in your home. To ensure that the coils function at their best, they should always be kept clean. Additionally, change the air filters as necessary.
3- Resonator Coils:
The outdoor unit’s major component for How AC works is where heat is delivered to the outside world. Regrettably, it is prone to collecting dirt and other debris, necessitating routine cleaning. As part of your summer planning, schedule an air conditioner maintenance.
4- Compressor:
This serves as the system’s beating center during How AC works. The refrigerant must pass through the evaporator coils and onto the condenser coils, and the pump ensures this happens, All year cooling duct cleaning.
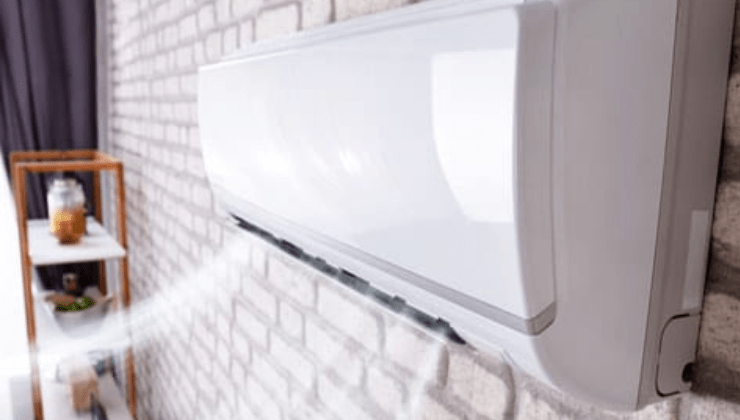
The Typical Cooling Process of an Air Conditioner
An air conditioner takes the following actions to guarantee that the cooling process is complete and tells us How AC works
:
The Thermostat signals the Need For Cooling
With a few button presses, the air conditioning procedure begins. You turn on your air conditioner and adjust the thermostat to the preferred setting. The sensors will be triggered and measure the temperature in your house. The thermostat will warn that the ambient temperature is too high, and the cooling cycle should start. The compressor will switch on to enable the refrigerant to begin its system-wide journey. The fans will also come to life.
More service: Chiller AC
The Refrigerant absorbs Heat From Indoor Air
You might think, How AC works? The evaporator coils are where the cold refrigerant ends. Here, it will come into contact with warm inside air and absorb the heat. As the refrigerant warms up, the air gets colder. The vapor will condense into the water if the air has excessive moisture. A dehumidifier is, therefore, a function of your air conditioner. It has a tray where the water is collected before being properly drained outside. By doing this, the water will not trickle into your unit and home, protecting your AC, floor, and walls from harm.
Fans Blow Cooler Air Back Into The Home
The evaporator coils are surrounded by cold air as the fan blows back into your house. If you have a central air conditioning system, the cold air is distributed evenly throughout the home through the ductwork. On the other hand, a window or split system will direct the cold air into the room where it is located. This enables you to regulate the temperature in different zones to accommodate the various needs of the residents. To use less energy, the indoor unit for each area can also be switched off while not in use.
The Refrigerant’s Internal Heat Is Released Outside
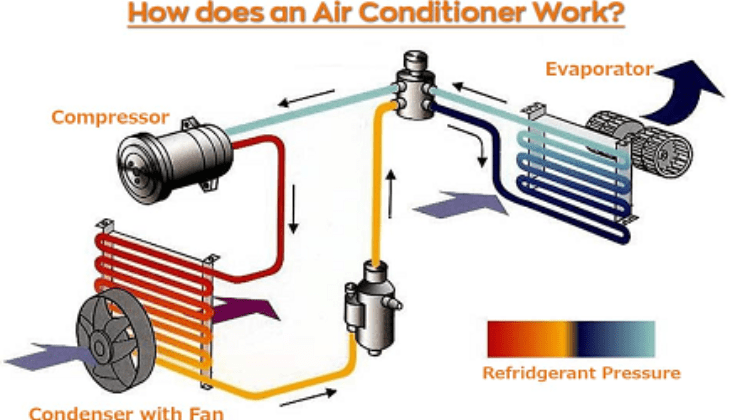
The refrigerant eventually reaches its limit while absorbing heat, just like a sponge. It must therefore dissipate the heat outside. The outdoor unit’s condenser coils transport it out to release the heat. As long as the refrigerant is hotter than the ambient temperature outside, it will continue to release heat. Only when a balance is attained will it come to an end.
Fans disperse the Hot Air
Intense fans blow air across the condenser coils, further assisting the refrigerant’s cooling process. Heat can get outdoors more quickly, thanks to the mechanism. When you approach the outdoor unit and feel the heat radiating, you will notice that the area around it is also getting hotter. The heat will dissipate in the breeze because it is in an open location, allowing your home to continue releasing internal heat to the neighborhood through the air conditioner.
The Indoor Unit Receives The Cold Refrigerant Once More
During the process of How AC works, the compressor pushes the refrigerant back to the interior unit once it reaches equilibrium so that the cycle can be repeated. The process will continue until the thermostat sensors determine that the inside temperature has reached the desired level. When the temperature in your home rises again, this will cause it to halt and rest. When this occurs, the AC will immediately restart the cooling operation.
Air Conditioner Types
As you can see, there are straightforward and highly complicated explanations for How AC works. The same applies to describing different kinds of air conditioners. Residential air conditioning systems are available in many designs and combinations to accommodate a wide range of indoor living spaces, from the newest tiny dwellings to 30,000-square-foot mansions. The three main varieties are split-system air conditioners, packaged air conditioners, and ductless air conditioners. While each has a unique set of applications, they all ultimately serve the same purpose: keeping your home cool.
Split Air Conditioner
The most frequent response to the query ‘How AC works’ is a split system. Both an indoor unit and an outdoor unit are part of these systems. The evaporator coil and blower fan (air handler) that circulate air throughout the residence are part of the interior unit, commonly a furnace or fan coil. The compressor and condenser coil are located in the outside unit.
Read More: How much does duct cleaning cost
Split-system air conditioners offer a range of options, including straightforward single-stage systems, more energy-efficient and quieter two-stage systems, and the most energy-efficient and quiet multi-stage systems. An entire home’s temperature can be reliably and consistently controlled using a split system air conditioner. The system can also clean your air while cooling it because the inside air handler uses filters.
Packaged AC
The evaporator coil, blower fan, compressor, and condensing coil are all included in packaged systems as a single unit. They function well when there isn’t enough room in an attic or closet for a split-system air conditioner’s interior unit. They are also a suitable option for locations where rooftop installations are favored. Like split systems, packaged systems use return air ducts to draw warm air from the house into the evaporator coil area. The cooled air is returned to the residence through supply air ducts after passing through the evaporator coil. Additionally, like with a split system, the condenser coil allows the surplus heat to be discharged outside.
Additionally, there are several alternatives for improved energy efficiency with packaged systems. Both single-stage and two-stage designs are available. Multi-speed blower fans are a feature of more efficient types.
Ductless AC

Because they only provide cooling to particular, targeted regions of the house, ductless systems are not considered central air systems. Because, as their name suggests, they don’t rely on ductwork to circulate chilled air, they require less intrusive installation. Ductless systems, like split systems, consist of at least one interior unit and one outdoor unit connected by copper refrigerant tubing. Each indoor unit in a ductless system is made to solely deliver cool air for the space in which it is installed. The interior unit can be mounted to the floor, a wall, or the ceiling. A single outside unit may be connected to several indoor units in some ductless systems. No matter how many interior units are present, the system operates similarly to a split system.
More services: AC duct cleaning Dubai
An evaporator coil and blower fan are included in the indoor unit to draw warm air out of the space, pass it over the cold evaporator coil, and then circulate the cooler air back into the space. Copper tubing transports refrigerant to the outside unit, which houses the compressor and condenser coil. The external condenser coil is used to expel heat that is trapped inside. The cycle continues as the refrigerant travels back to the indoor unit.
These adaptable systems provide precise comfort where indoor units are installed. By allowing for individual temperature control over each separate room, they also function like a zoning system. Install a ductless unit in each room, for instance, if you prefer a warmer bedroom but a cooler home office. Depending on your comfort preferences, you can select different temperatures in each space.
Conclusion
By now, you might’ve known How AC works. It does not produce chilly air while the air conditioner is on. Instead, it gradually extinguishes the heat from your home until the atmosphere is sufficiently chilled. The intelligent design of an air conditioning system has been in use for decades. Technology advancements have pushed for more energy-efficient versions, allowing your home to use less power while being more comfortable.